BT LAB Biomarkers for Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in lung tissues. Most lung carcinomas derive from cancerous bronchia mucosal epithelium cells The molecular characterization of lung cancer has considerably changed the classification and treatment of these tumors, becoming an essential component of pathologic diagnosis and oncologic therapy decisions. (P Villalobos, 2016)
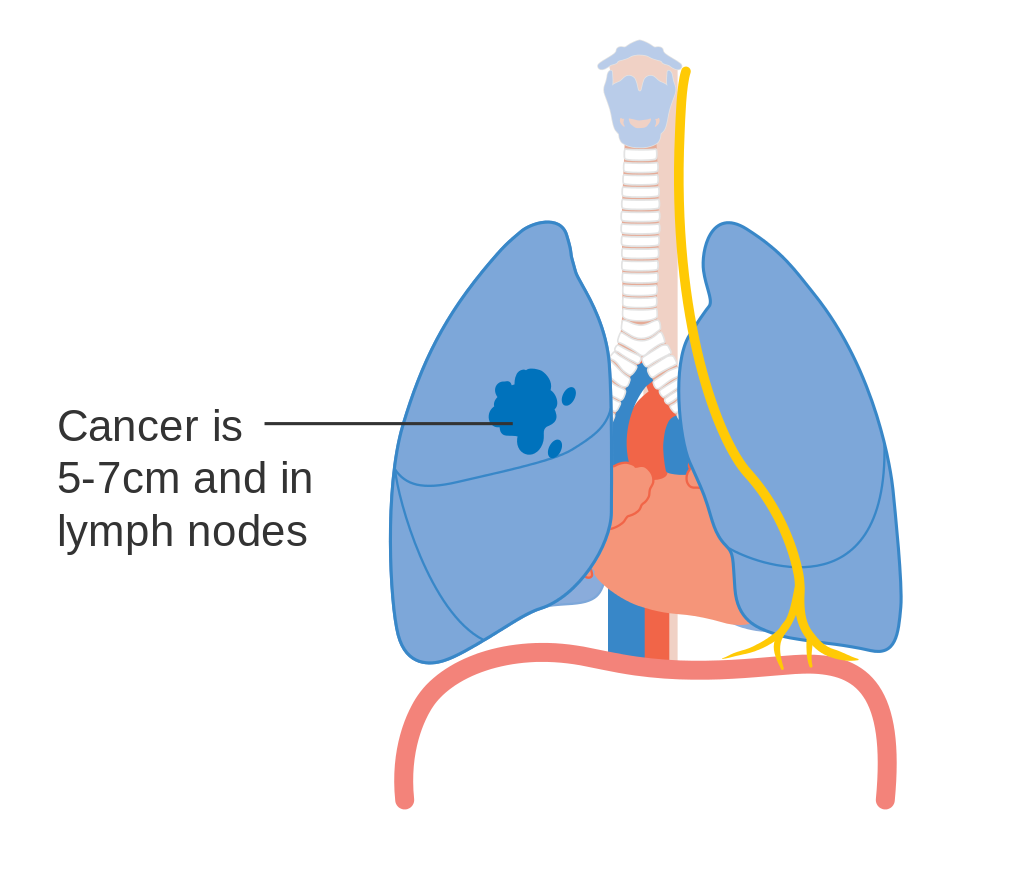
Stage IIB lung cancer
Let's take a look at BT-LAB’s markers for lung cancer.
PD-L1
PD-L1 expression on tumour cells can guide the use of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune modulators to treat patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression both within and between tumour sites is a well-documented phenomenon that compromises its predictive power. (A.Haragan. 2019)
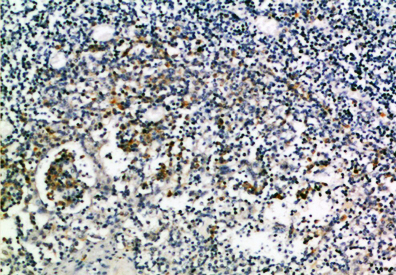
BT-AP14816-PD-L1 Polyclonal Antibody
CD01142-Recombinant Human PD-L1 (19-239) protein (C-6His)
CD01141-Recombinant Human PD-L1 (19-239) protein (C-Fc)
EGFR
Epidermal growth factor receptor is a trans-membrane glycoprotein with an extracellular epidermal growth factor binding domain and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain that regulates signaling pathways to control cellular proliferation. Epidermal growth factor receptor binding to its ligand results in autophosphorylation by intrinsic tyrosine/kinase activity, triggering several signal transduction cascades. Constitutive or sustained activation of these sequences of downstream targets is thought to yield more aggressive tumor phenotypes.Mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor have been discovered in association with some lung cancers. Lung adenocarcinomas with mutated epidermal growth factor receptor have significant responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors, although for unselected patients it does not appear to have a survival benefit. However, in a subset of patients (non-smoking Asian women with adenocarcinoma, particularly with a bronchioloalveolar carcinoma), there appears to be a significant survival advantage. (G. Bethune.2010)
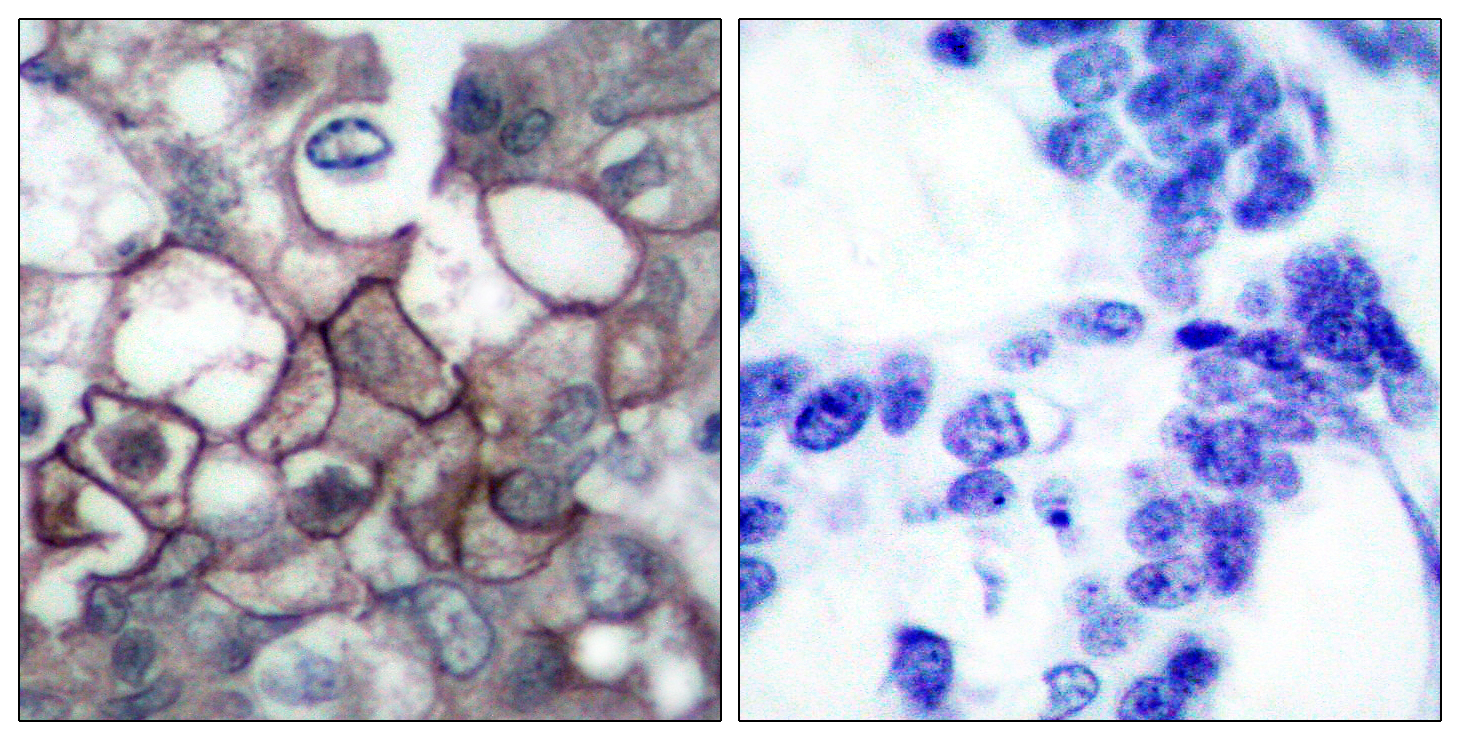
BT-MCA0467-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody(1B10)
BT-MCA0468-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody(M6)
BT-AP08766-EGFR Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP15381-EGFR Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP15380-EGFR Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP15379-EGFR(Phospho-Tyr998) Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP15378-EGFR(Phospho Tyr869) Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP08759-EGFR(Phospho Tyr1197) Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP00565-EGFR(Phospho Ser1026)Polyclonal Antibody
SOX2
SOX2 is a stem cell transcription factor that plays a crucial role in the regulation of embryonic development. It is one of the genes in a set of factors (Oct4, SOX2, Nanog) that are able to reprogram human somatic cells to pluripotent stem cells. Overexpression of SOX2 has been described in all types of lung cancer tissues, including small cell and squamous cell carcinoma but also adenocarcinoma. An in-depth view of the spectrum of genomic alterations in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has identified SOX2 as a potential target for therapeutic intervention. (N. Karachaliou. 2013)
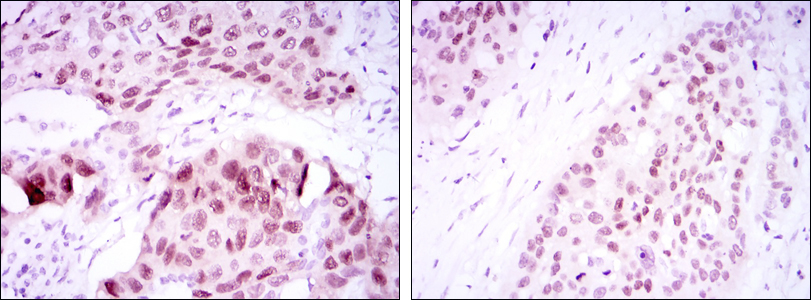
BT-MCA1152-SOX-2 Monoclonal Antibody
BT-MCA1153-SOX-2 Monoclonal Antibody
BT-MCA1154-SOX-2Monoclonal Antibody
BT-AP12725-SOX2(Phospho-Ser250/Ser251) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
P63
p63 is a recently discovered member of the p53 family that has been shown to be important in the development of epithelial tissues. p63 may also play a role in squamous cell carcinomas of the lung, head and neck, and cervix, and its expression is increased in these tumors. (N H C Au.2004)
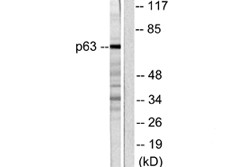
BT-MCA0980-p63 Monoclonal Antibody
BT-AP12689-p63(Phospho Ser455) Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP12688-p63(Phospho Ser395) Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP11745-p63(Phospho-Ser160/162) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP06845-p63 Polyclonal Antibody
BT-AP06846-p63 Polyclonal Antibody
